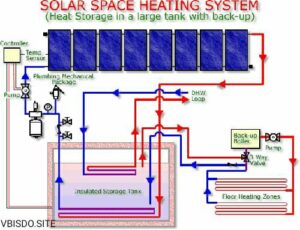
Recently, solar heating systems have become somewhat well-known as a greener substitute for conventional heating systems. Many times, they are commended for cutting carbon emissions, decreasing energy costs, and solar renewable energy use. Solar heating systems do, however, have some difficulties and disadvantages, much like any technology.
Understanding the drawbacks of solar heating systems will help you to decide whether or not to make the investment. Covering everything from installation costs to maintenance needs, this article investigates the major drawbacks of solar heating systems.
1. Strong Initial Installation Cost
The initial outlay of solar heating systems is among their most often mentioned drawbacks. Expensive purchases and installation of solar thermal panels, storage tanks, pumps, and control systems is involved. Initial expenses, depending on the kind and scale of the system, may run from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Although many governments provide tax credits, subsidies, or incentives to help with these costs, the initial financial load still discourages many firms and homes.
2. Temperature Dependency
Effective operation of solar heating systems depends on sunshine. This makes their reliance on local temperature and weather conditions somewhat great. Solar heating systems may function much less in areas with little sun exposure, plenty of overcast days, or lengthy winters.
Seasonal fluctuation may affect the availability of solar energy even in bright areas, so depending only on solar heating at certain periods of the year becomes challenging. In these situations, a backup system like electric or gas heaters might be required, therefore raising general expenses.
3. Restricted Cold Climate Efficiency
Although solar panels need not high temperatures to operate, their effectiveness decreases in cooler areas. Solar collectors may suffer from snow, ice, and cold conditions. Snowfall may obscure panels, thereby lessening of solar absorption. Moreover, fluid in the pipes might freeze and, in case of inadequate insulation, cause possible damage or system breakdown.
Long-term expenses from solar thermal systems might include more regular maintenance in colder climates and specific antifreeze treatments.
4. High Space Demand
Particularly those designed to provide hot water or heat for whole homes or businesses, solar heating systems need for a lot of ground or roof area. The heating demand will determine how many solar thermal collectors are required; for bigger buildings, this might be somewhat high.
Not every real estate has enough room for installation. The usefulness of the system may be hampered by architectural restrictions, shaded roofs, or lack of appropriate angles.
5. Issues with Storage
Large storage tanks are often needed in solar heating systems to store hot water for usage during times of little or none of sunshine. These tanks occupy important space and need to be effectively insulated to reduce heat loss.
Still a technical difficulty is effectively storing heat over long times. Particularly for long-term usage, thermal storage is large and less efficient than power from solar PV systems, which may be kept in small batteries.
6. Repair and Maintenance Costs
Solar heating systems need regular maintenance to be effective even if their maintenance is somewhat minimal when compared to conventional heating systems. Regularly examined components include pumps, valves, sensors, and antifreeze fluid.
Particularly in severe weather, system components might gradually deteriorate or get destroyed. System efficiency may be lowered, for instance, by pipe leaks or declining collector performance. Either replacing or fixing these parts might be costly and call for professional knowledge.
7. System Complexity
Collectors, circulation pumps, controllers, and storage tanks are among the many linked elements of a full solar heating system. This increases the complexity of the system relative to traditional heating systems.
This intricacy may make troubleshooting difficult as well as installation demanding. Not all HVAC specialists are qualified to operate solar thermal systems, thus in certain places your access to seasoned experts may be limited.
8. Divergent Performance
Performance variances in solar heating systems are another problem. System efficiency may be impacted by elements such panel angle, collector type, shadowing from surrounding buildings or trees, and even dust on the collectors.
This makes it difficult to precisely estimate heating effectiveness as the output of your solar heating system might fluctuate significantly day to day or season to season. Homeowners can discover they depend more on supplemental heating than first thought.
9. Not Perfect for Every Heating Need
Underfloor heating or low-temperature space heating—that is, for domestic hot water (DHW)—usually fits solar heating systems. For high-temperature uses like industrial operations or demand commercial heating without major changes, they are not efficient.
This restriction makes them less flexible than conventional gas or electric systems that can meet a greater spectrum of heating demand.
10. Long Payback Times
Though long-term energy cost reductions abound, solar heating systems have a quite lengthy payback period—often 7 to 15 years or more. This is particularly true in case of low local energy costs or insufficient solar subsidies.
The investment could not provide enough profit until the house is sold for homeowners who want to relocate in the near future. Furthermore, some possible purchasers may not see value in a solar thermal system and would even consider it as a maintenance burden.
11. Production Environmental Effects
Although solar heating systems are promoted as ecologically benign, the fabrication of solar thermal components—especially metals like copper and aluminum—involves energy use and raw material extraction. These procedures help to produce greenhouse gases and pollutants.
Moreover, the systems have a limited lifetime (typically 20–30 years), hence improper handling of components might lead to environmental problems regarding disposal or recycling.
Finish
Although solar heating systems have many benefits—especially in terms of lowering your carbon footprint and long-term power bills—they are not without flaws. Important factors include the high initial cost, climatic dependability, space constraints, storage restrictions, and maintenance demands.
Thus, what are the drawbacks of systems of solar heating? In general:
-
large initial expenses
-
Climate and dependability of the weather
-
effective in places with cold or clouds
-
Requirements for storage tanks and big space
-
Frequent upkeep and sporadic fixes
-
Simplicity in design and implementation
-
Inconsistent output
-
restricted adaptability
-
long duration of return on investment
-
Production and disposal environmental issues
Examine your local climate, budget, available space, and energy requirements carefully before settling on a solar heating system. See a qualified solar energy consultant to evaluate whether a solar heating system would be appropriate for your house or company.